William John Macquorn Rankine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Rankine
William Rankine - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Scottish mechanical engineer William John Macquorn Rankine FRSE FRS (; 5 July 1820 – 24 December 1872) was a Scottish mechanical engineer who also contributed to civil engineering, physics and mathematics. He was a f
en.wikipedia.org
(1820~1872, Scotland)
Rankine's theory (maximum-normal stress theory), developed in 1857
Rankine 토압의 가정
흙은 비압축성이고 균질한 입자이다.
흙입자는 입자간의 마찰력에 의해서만 평형을 유지한다.
지표면은 무한히 넓게 존재한다.
지표면에 작용하는 하중은 등분포하중이다.
토압은 지표면에 평행하게 작용한다.
Assumptions of Rankine Theory of Earth Pressure-
1. The soil is considered to be homogeneous, isotropic, semi-infinite, elastic, dry and cohesionless (i.e. this theory is valid only for cohesionless soils like sand and not for cohesive soils like clays)
2. The ground surface is considered to be planar, which may be horizontal or inclined.
3. The face of the wall in contact with the backfill is considered vertical and smooth.
4. The soil is considered to be in the state of plastic equilibrium in active and passive earth pressure conditions.
5. The rupture surface is considered to be planar.
6. There is no wall friction.
7. The normal and shear forces acting on the back of the wall result in an angle parallel to the ground surface.
Resal (1910) and Bell (1915) extended Rankine’s theory of earth pressure for cohesive soils
Rankine's active earth pressure
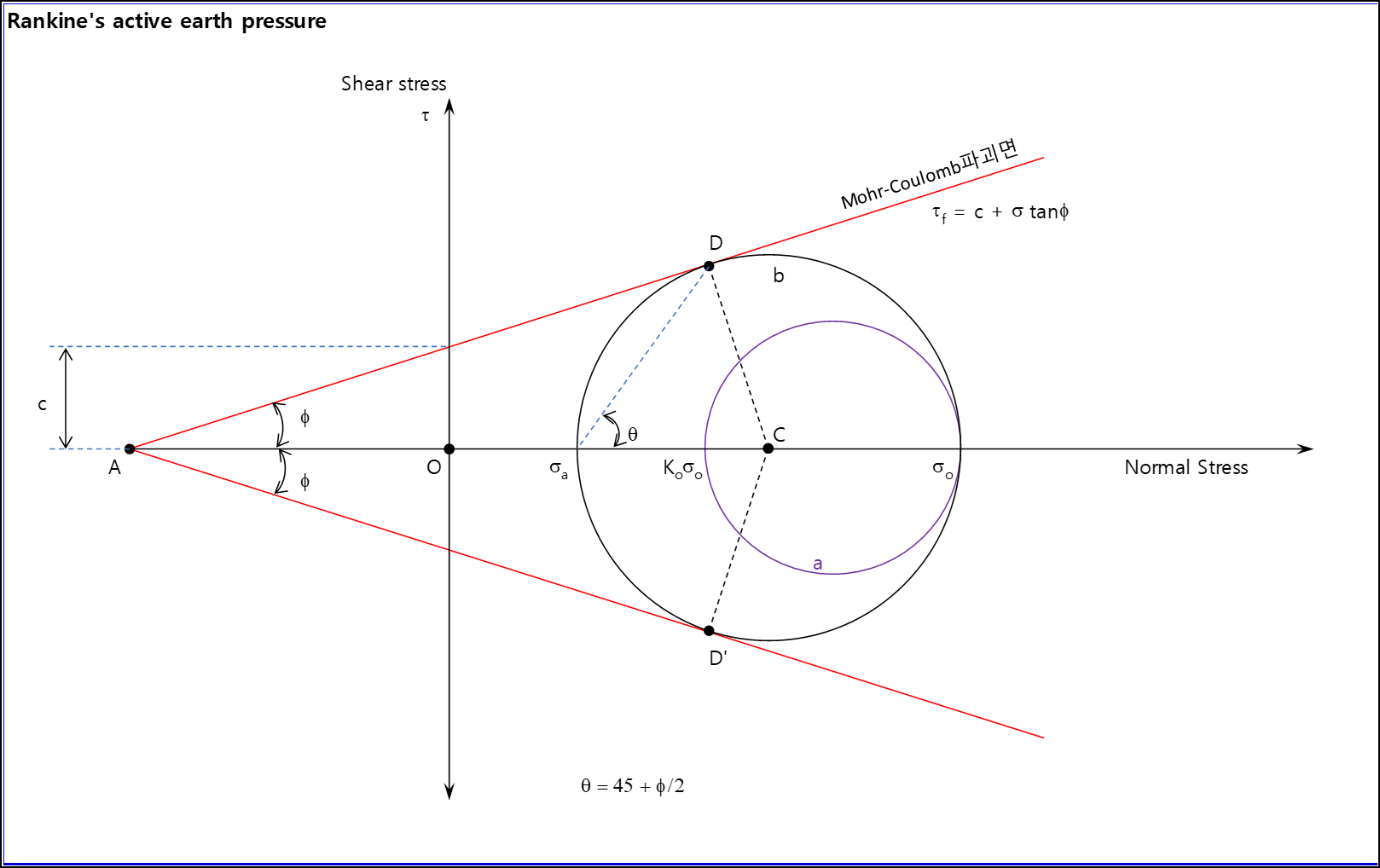
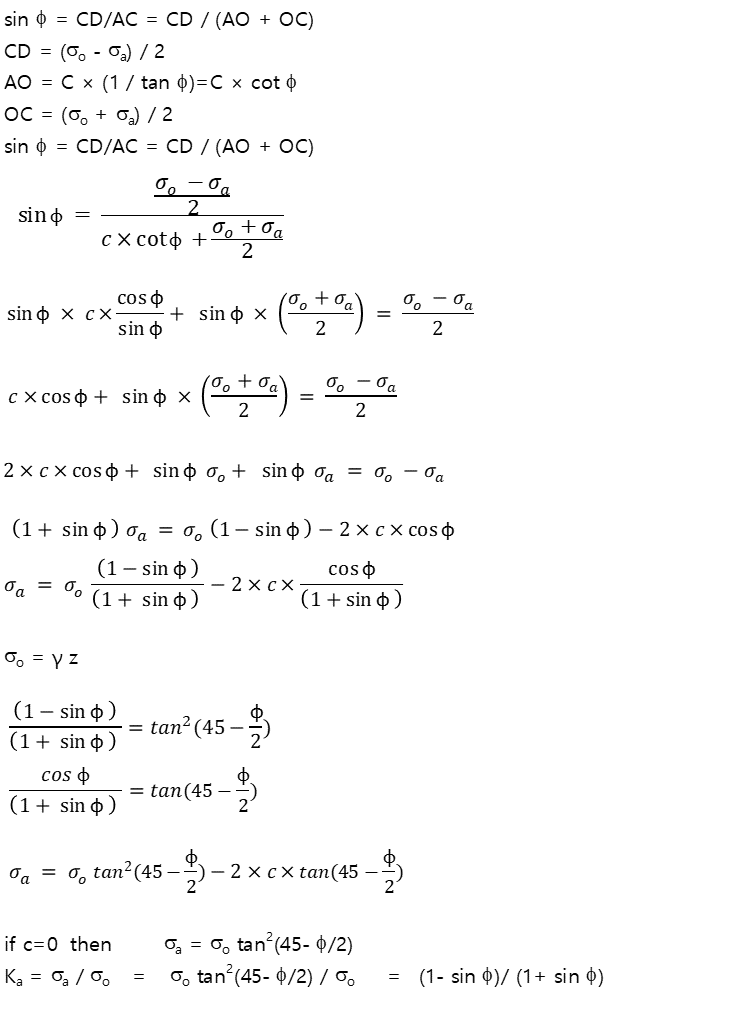
θ = 45° - Φ/2 (흙의 파괴면과 수평면이 이루는 각)
Rankine's passive earth pressure
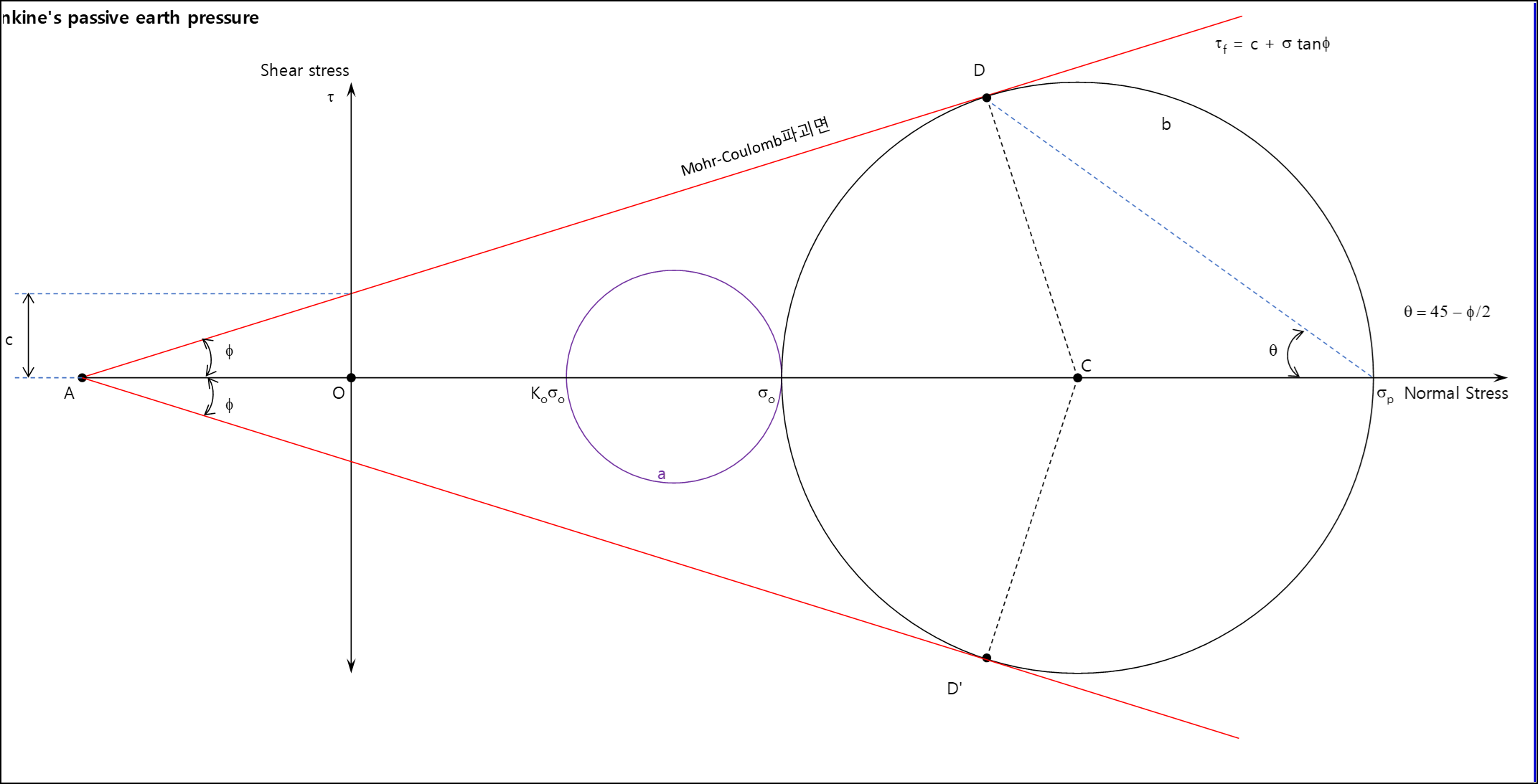
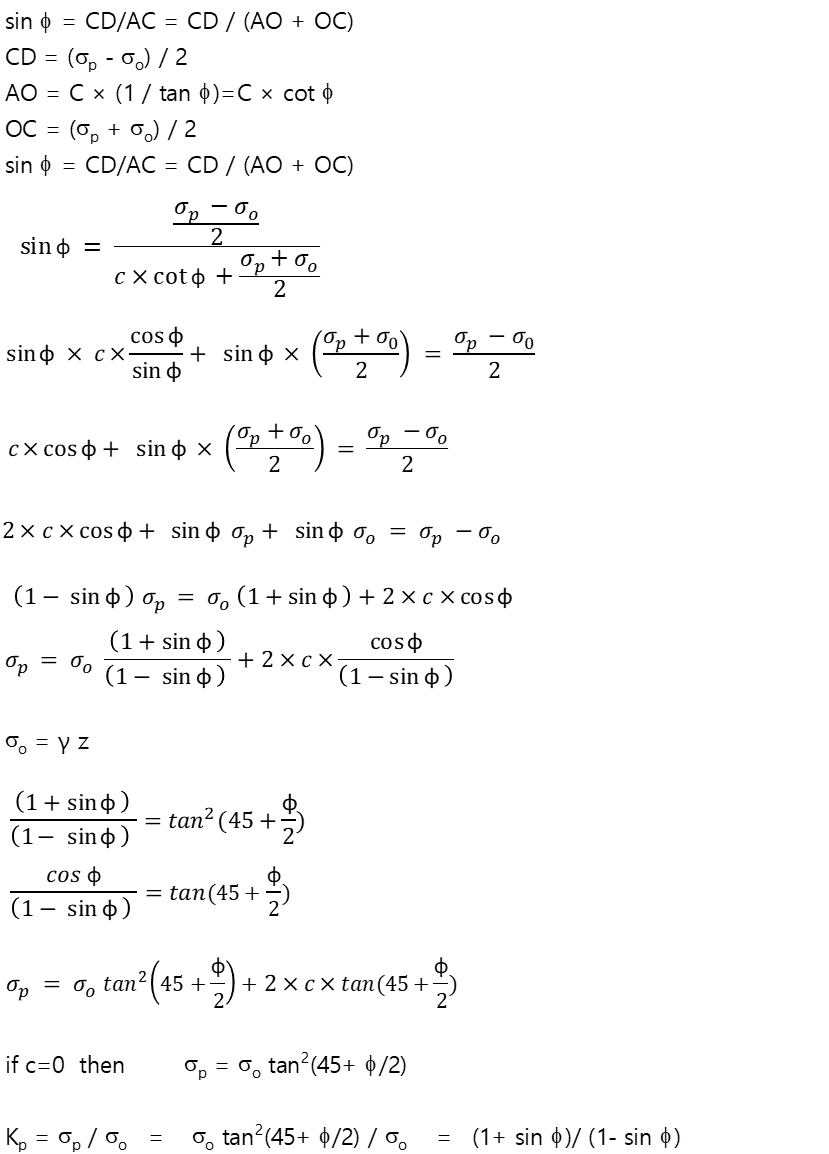
θ = 45° - Φ/2 (흙의 파괴면과 수평면이 이루는 각)
Rankine active and passive pressure with sloping backfill
Rankine's active earth pressure for a retaining wall with a cohesionless backfill with a sloping surface

Rankine's passive earth pressure for a retaining wall with a cohesionless backfill with a sloping surface

Rankine active and passive pressure with a sloping backfill & a cohesive backfill
Rankine's active earth pressure for a retaining wall with a cohesive backfill and a sloping surface
토압계산 관련
2022.01.04 - [ 업무관련] - coulomb wedge theory 쿨롱 시행쐐기법
2022.01.08 - [ 업무관련] - coulomb wedge theory 쿨롱 시행쐐기법 excel
2022.01.22 - [ 업무관련] - MONONOBE-OKABE AND COULOMB EQUATIONS
2022.09.20 - [ 업무관련] - culmann의 도해법
2022.12.26 - [ 업무관련] - 절토부 옹벽에 작용하는 토압
2023.04.18 - [ 업무관련] - 절토부 옹벽의 토압계산
https://www.kgsjournal.org/articles/xml/K9ge/#
The Calculation and Design Method of Active Earth Pressure with Type of Gravity Structures
Copyright © 2014 by the Korean Geotechnical Society ABSTRACT 1. 서 론2. 이론 고찰 2.1 토압이론 2.1.1 Rankine 토압론 2.1.2 Coulomb 토압론 2.1.1 Rankine 토압론 2.1.3 시행쐐기론 2.1.4 개량시행쐐기론 2.1.5
www.kgsjournal.org
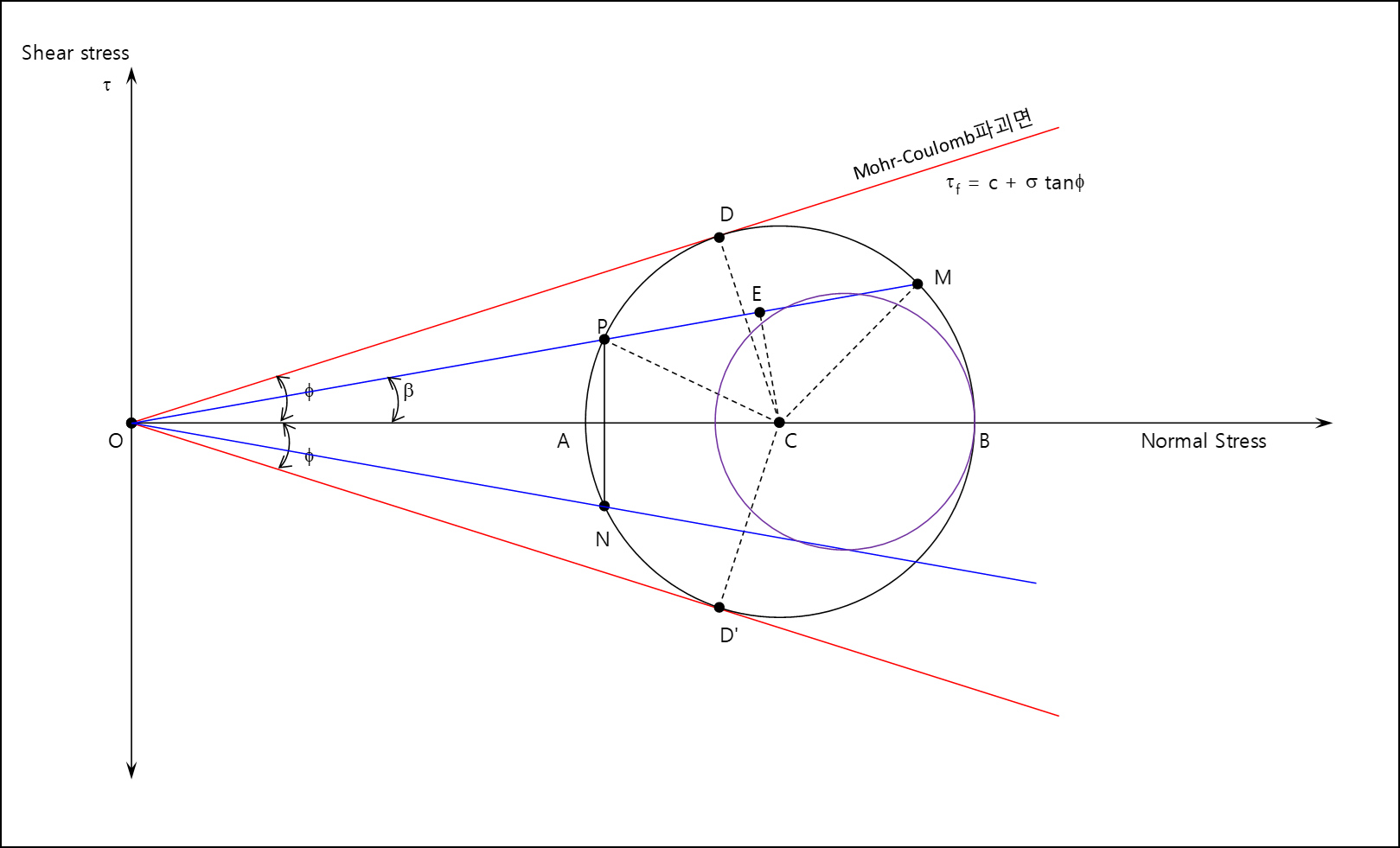
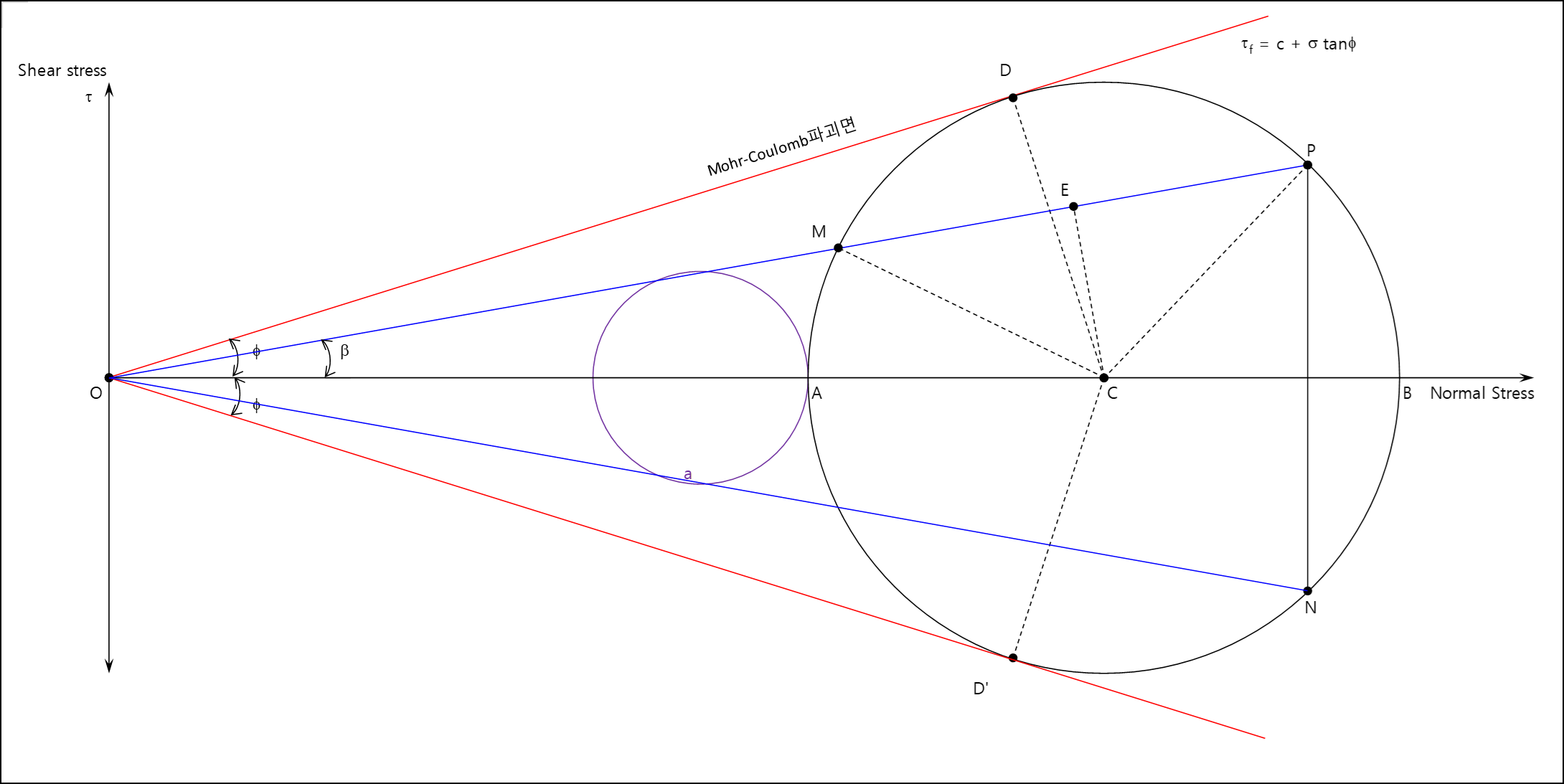
Rankine's Theory of Active Earth Pressure | Soil
ADVERTISEMENTS: Rankine (1857) considered the equilibrium of a soil element at any depth (h) in the backfill behind a retaining wall and determined the active earth pressure. Rankine assumed that the soil element is subjected to only two types of stresses:
www.soilmanagementindia.com
Rankine's Theory of Passive Earth Pressure | Soil
ADVERTISEMENTS: In the passive case, the retaining wall moves toward the soil, causing compression of the soil and increasing the lateral earth pressure. When the soil reaches the state of plastic equilibrium, the Mohr’s circle touches the Coulomb’s
www.soilmanagementindia.com






최근댓글