Concrete – Complementary British Standard to
BS EN 206-1 – Part 1: Method of specifying and guidance for the specifier
Table A.1 Exposure classes

Reinforced and prestressed concrete walls and structure supports within 10 m of a carriageway
Bridge parapet edge beams
Buried highway structures less than 1 m below carriageway level
Reinforced pavements and car park slabs
KDS 24 14 21에서는 다음과 같이 설명하고 있다.
이것은 차도로부터 6m 이내에 있는 모든 난간, 벽체, 교각을 포함하며, 또한 차도로부터 배출되는 물에 노출되기 쉬운 신축이음부(expansion joints) 하부 교각의 윗부분과 같은 표면을 포함한다.
Concise Eurocode 2 for Bridges
https://www.concretecentre.com/TCC/media/TCCMediaLibrary/Events/Online%20course/CCIP_EC2_Bridges.pdf
4 Durability and cover
4.1 Grneral

여기서 말하는 차도로 부터 수평방향 10m 이내와 높이방향 5m이내는
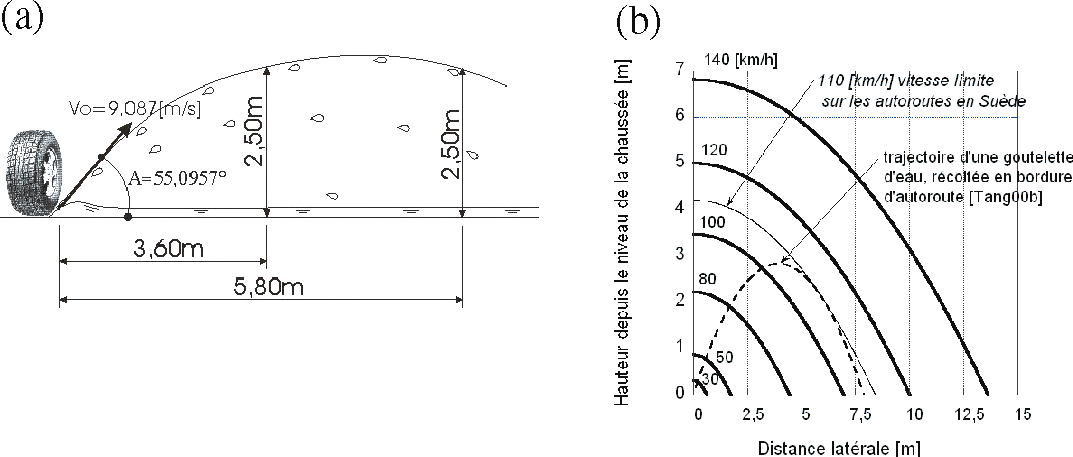
Droplet projection pattern as a function of mean vehicle speed, with dashed lines showing the basic trajectory of the model, derived from the collection of water in droplets at different ground levels and roadside distances (Tang and Utgenannt 2000)에서 제시된 그래프와 같다.
2024.04.16 - [업무관련] - 평균 차량 속도와 물방울 투영 패턴
EN 1992-2 4.2(106)
4.2 Environmental conditions
(104) Water penetration or the possibility of leakage from the carriageway into the inside of voided structures should be considered in the design.
(105) For a concrete surface protected by waterproofing the exposure class should be given in a Country’s National Annex.
NOTE For surfaces protected by waterproofing the exposure class for use in a Country may be found in its National Annex. The recommended exposure class for surfaces protected by waterproofing is XC3.
(106) Where de-icing salt is used, all exposed concrete surfaces within x m of the carriageway horizontally or within y m above the carriageway should be considered as being directly affected by de-icing salts. Top surfaces of supports under expansion joints should also be considered as being directly affected by de-icing salts.
NOTE 1 The distances x and y for use in a Country may be found in its National Annex. The recommended value for x is 6m and the recommended value for y is 6m.
NOTE 2 The exposure classes for surfaces directly affected by de-icing salts for use in a Country may be found in its National Annex. The recommended classes for surfaces directly affected by de-icing salts are XD3 and XF2 or XF4, as appropriate, with covers given in Tables 4.4N and 4.5N for XD classes.
KDS 24 14 21와 EN 1992-2 4.2(106)에서 추천값으로 수평방향(x)는 6m, 수직방향(y)는 6m로 되어 있다.
Tang and Utgenannt 2000에서 제시한 그래프에서 x=6m와 y=6m를 그려보면 그 범위는 다음 그림과 같다.

DESIGNERS' GUIDE TO EN 1992-2
EUROCODE 2 : DESIGN OF CONCRETE STRUCTURES
PART 2: CONCRETE BRIDGES
4.2. Environmental conditions
Parts of bridges exposed to spray containing chlorides including surfaces within 6m (horizontally or vertically) of a carriageway where de-icing salts are used (e.g. parapets, walls and piers) and surfaces (such as the top of piers at expansion joints) likely to be exposed to water draining/leaking from the carriageway. EN 1992-2 clause 4.2(106) refers
여기서 Carriageway는 무엇을 말하는 것일까? 길어깨를 포함한 것일까?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carriageway
Carriageway - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Width of road on which a vehicle is not restricted by any physical barriers Diagram showing different arrangements of the elements of a road An intersection of the German A7 Autobahn near Hamburg showing slip roads as
en.wikipedia.org
A carriageway (British English)[1] or roadway (North American English) [2] consists of a width of road on which a vehicle is not restricted by any physical barriers or separation to move laterally.
A carriageway generally consists of a number of traffic lanes together with any associated shoulder, but may be a sole lane in width (for example, a highway offramp).
ChatGPT의 답변은 다음과 같다.
"Carriageway" typically refers to the part of a road intended for vehicles to travel on. It generally includes the main traveled portion of the road but does not typically include the shoulder. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
- Carriageway: This is the part of the road designed for the movement of vehicles. It includes the lanes used for vehicular traffic but usually excludes the shoulder.
- Shoulder: This is the area adjacent to the carriageway. It is often used for emergency stops, breakdowns, and sometimes for pedestrians and cyclists.
In many road design standards and guidelines, the carriageway is distinct from the shoulder. The shoulder is considered a separate part of the road infrastructure, serving different functions such as emergency stopping space and lateral support for the pavement.
In specific contexts or regulatory documents, the exact definition and what is included in the carriageway might vary slightly, but generally, the shoulder is not included in the carriageway.
In EN 1990, "carriageway" refers to the part of a road used by vehicular traffic. This definition typically includes the lanes on which vehicles drive, but does not necessarily include the road shoulders, footpaths, or other adjacent areas. The specific use and extent of the term "carriageway" can vary depending on the national or regional guidelines that supplement the main Eurocode documents (Merriam-Webster) (Educalingo).
For further details, the Eurocode standards and associated national annexes provide comprehensive guidelines and definitions.
#염화물의 영향을 받는 범위
#차도로부터6m
2024.04.16 - [업무관련] - 평균 차량 속도와 물방울 투영 패턴








최근댓글